
45-Year-Old Male with Uncontrolled Hypertension
February 14, 2024
70-Year-Old Female with Chronic Kidney Disease and Hypertension
February 14, 2024Personalized Treatment Regimen Following Pulse Wave Analysis
58-Year-Old African American Female with Diabetes and Uncontrolled Hypertension
Patient Medical History
- 58-year-old African American female with diabetes mellitus
- Current Rx Regimen:
- Amlodipine 10 mg daily
- Clonidine patch #2 once weekly
- Lisinopril 20 mg daily
- Rosiglitazone 30 mg daily
- Metformin 1000 mg daily
- Simvastatin 20 mg daily
- Aspirin 81 mg daily
Initial Digital Vascular Biomarker Assessment
| Brachial Blood Pressure | 220/103 mmHg |
| Central Systolic Pressure | 202 mmHg |
| Central Pulse Pressure Amplification | 19% |
| Augmentation Index | 31% |
| Heart Rate | 70 bpm |
Initial Assessment Interpretation
This patient’s central pressure profile indicates a pulse pressure amplification of 19%. The central systolic pressure of 202 mmHg is much more than the desired value of 124 mmHg. The Augmentation Index (A) is 31%. In this patient’s scenario, a clear second peak in the aortic pressure contour just above 170 mmHg is present, along with a systolic pressure of 202 mmHg. This indicates that about 30 mmHg of the 98 mmHg, ie, AIx of approximately 31%, central pulse pressure is augmented pressure.
Figure 13. Central Pressure Waveform
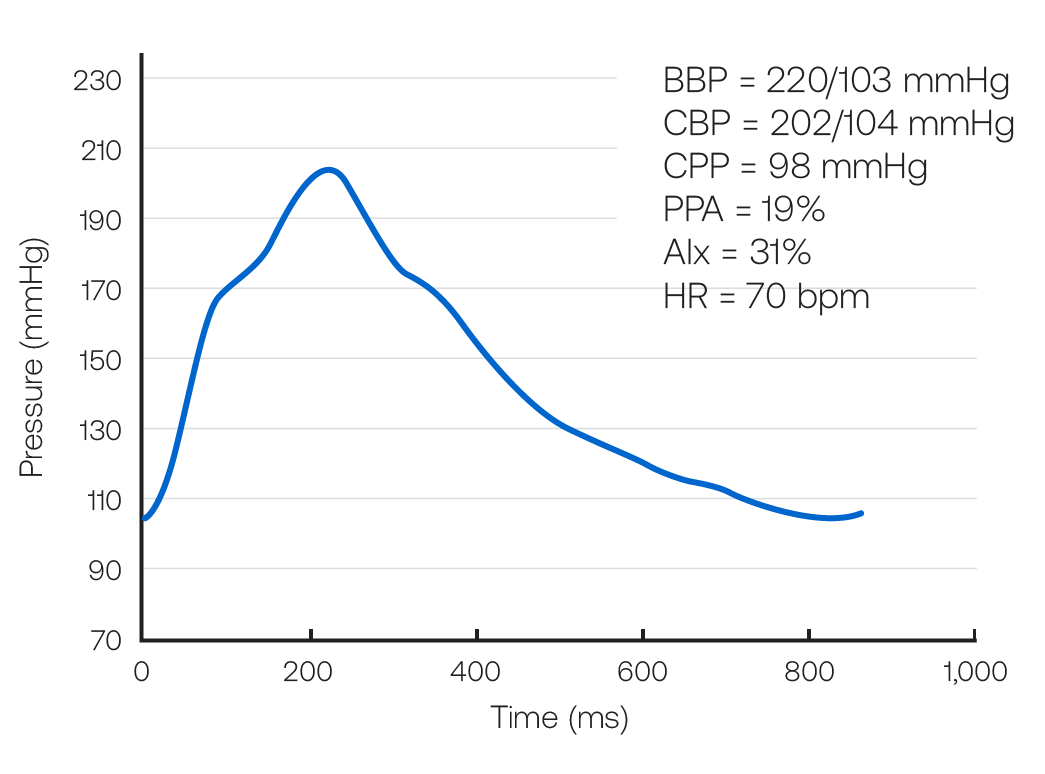
BBP indicates brachial blood pressure systolic/diastolic; CBP, central blood pressure systolic/diastolic; CPP, central pulse pressure; AIx, augmentation index; HR, heart rate; bpm, beats per minute.
Intervention
The approach is an emphasis on vasodilation while trying to preserve heart rate, with the goal to improve pulse pressure amplification while reducing brachial blood pressure. The nitric oxide–promoting ß-blocker nebivolol 5 mg is started, amlodipine dosage (after discussion with the patient) is increased to 20 mg daily, and combination hydrochlorothiazide/spironolactone 25 mg/25 mg is added. Her clonidine patch is tapered and discontinued.
Follow Up Digital Vascular Biomarker Assessment
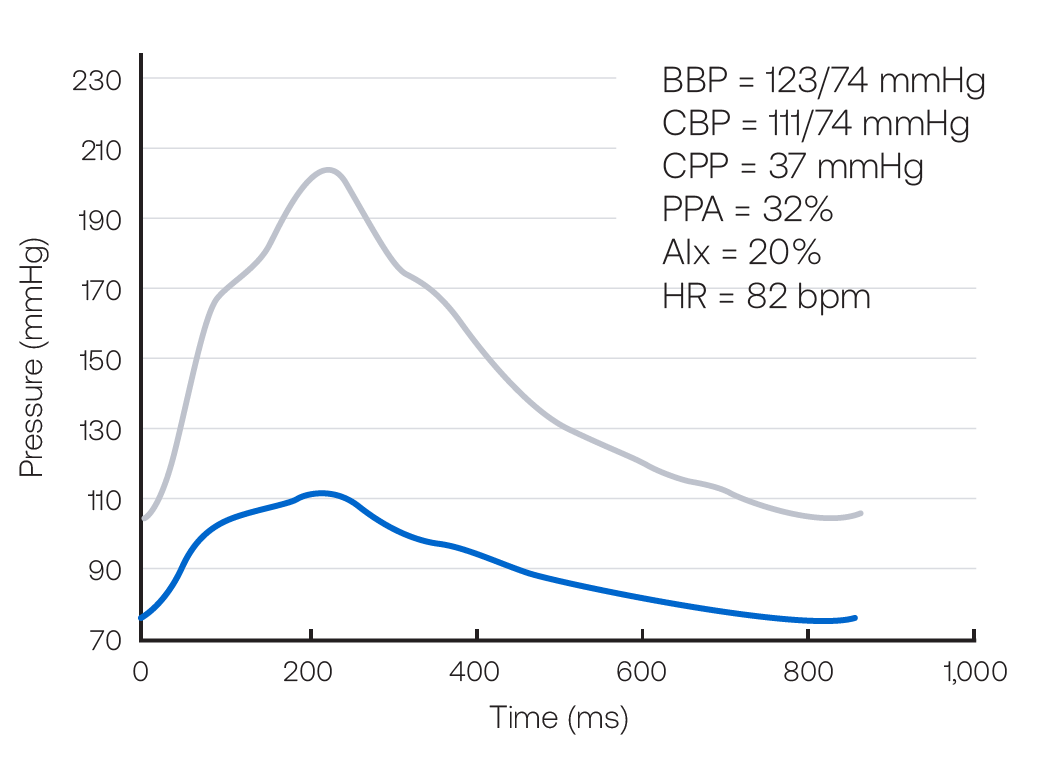
| Brachial Blood Pressure | 123/74 mmHg |
| Central Systolic Pressure | 111 mmHg |
| Central Pulse Pressure Amplification | 32% |
| Augmentation Index | 20% |
| Heart Rate | 82 bpm |
Follow up Assessment Interpretation
This female patient’s central pressure profile now shows a pulse pressure amplification of 32%. The central systolic pressure of 111 mmHg is less than the desired value of 124 mmHg. The AIx is reduced from 31% to 20%. No further changes were made. In this instance, the central pressure profile is used to help guide alteration of her regimen, which includes the addition of a ß-blocker and other changes, without the loss of a desirable central pressure profile.
*Townsend RR et al. Journal of Clinical Hypertension. 2015; 17:7, 503–513.
http://bit.ly/2gc5mdD
Figure 14. Central Pressure Waveform
Other Case Studies

