| |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Heart Rate (HR) |
The number of heart beats per minute and can indicate cardiac health and fitness levels. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Brachial Blood Pressure |
The pressure of blood in the brachial artery in the upper arm, an indicator of cardiovascular health. |
|
|
|
P |
|
 |
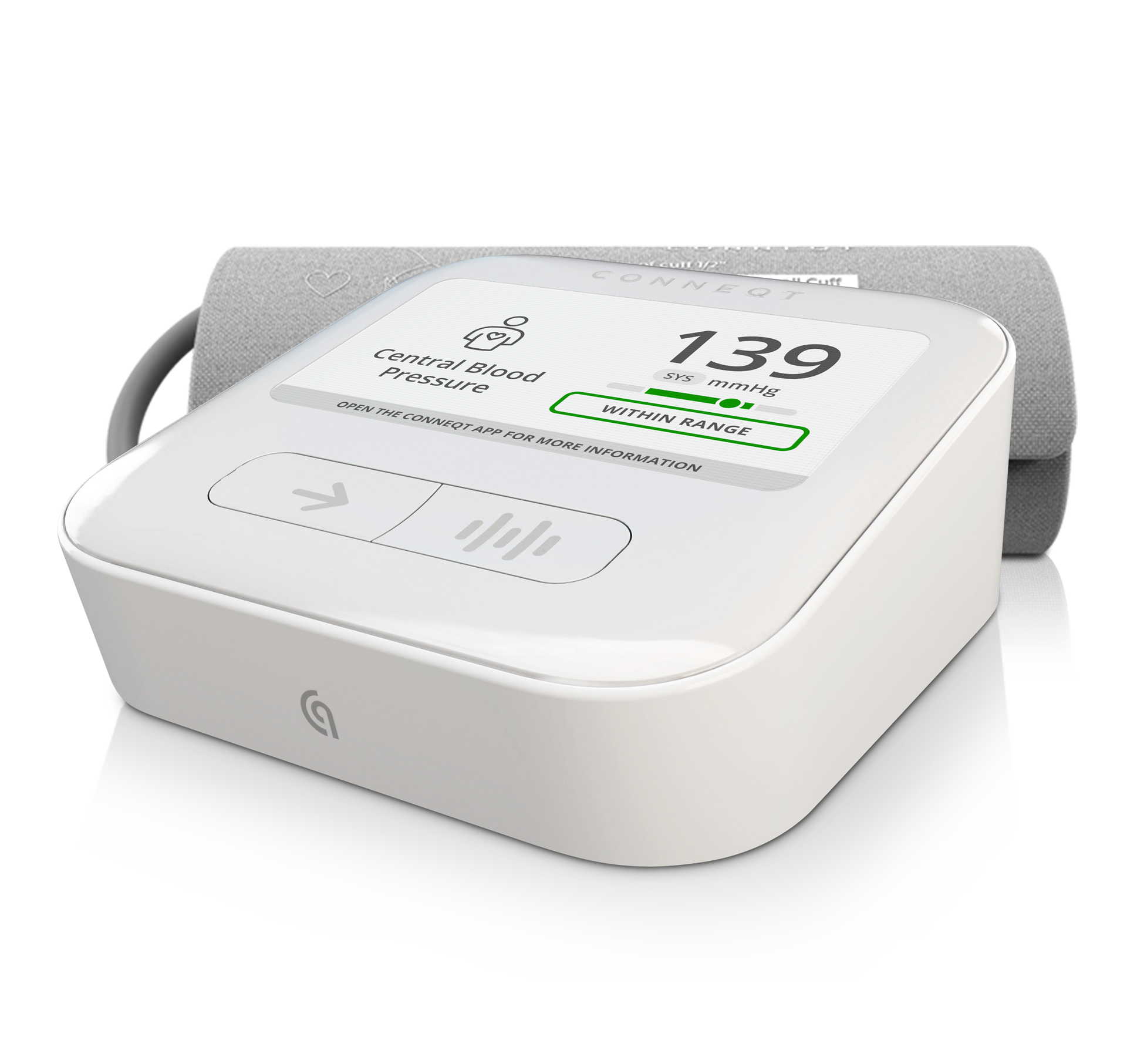
Central Blood Pressure (SP & DP) |
The pressure of blood at the root of the aorta, providing a more accurate assessment of cardiovascular risk compared to brachial blood pressure alone. |
|
|
|
P |
|
 |
Central Pulse Pressure (PP) |
The pressure experienced by major organs like the heart, brain, and kidneys, signaling the risk of end-organ damage. |
|
|
|
P |
|
 |
Augmentation Pressure (AP) |
The additional pressure exerted by the heart to overcome rigidity in the arterial wall, reflects both arterial stiffness and the extra workload on the heart. |
|
|
|
P |
|
 |
Augmentation Index (AIx) |
An assessment of the relationship between AP and PP to indicate the extent to which arterial stiffness influences the overall pressure experienced within the arterial system. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Subendocardial Viability Ratio (SEVR) |
A measure the balance between blood supply and demand in the inner heart muscle, offering insights into cardiac function under stress. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Pulse Pressure Amplification (PPA) |
The increase in amplitude of arterial pulse waves as they travel from central to peripheral arteries, providing insights into arterial stiffness and blood flow efficiency. |
|
|
P |
|
|
 |
Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) |
The speed at which the arterial pulse travels through the circulatory system, a key indicator of arterial stiffness. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
SphygmoCor Reference Age |
Estimates arterial age based on central pressure and arterial stiffness parameters, providing a reference for comparison with healthy individuals. |
|
|
P |
P |
|
 |
Spot check at point-of-care or home |
Monitoring conducted directly where the patient is, whether it's in a clinic or at home. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Ambulatory Monitoring |
Continuous observation and recording of physiological parameters, typically outside of a clinical setting, allowing for data collection during normal daily activities. |
|
|
|
|
|