
63-Year-Old Male with Hypertension and Low Augmentation Index
February 14, 2024
33-Year-Old Male with Persistent Systolic Hypertension*
February 14, 2024Personalized Treatment Regimen Following Pulse Wave Analysis
61-Year-Old Male with Hypertension and Comorbidities
Digital Vascular Biomarker Assessment
| Brachial Blood Pressure | 135/59 mmHg |
| Central Systolic Pressure | 124 mmHg |
| Central Pulse Pressure | 64 mmHg |
| Augmentation Index | 43% |
Interpretation
Pulse wave analysis on this male patient reveals very stiff arteries resulting in significant pressure wave reflection and left ventricle afterload. This patient also has a central pulse pressure (cPP) biomarker well above the threshold risk level of 50 mmHg,* that translates to a 20% increase in event rates in this population at 5 years. This is equivalent to the event rate at 10 years for the high-risk classification under the Framingham risk score. Vasodilating medications (ACEi, ARB, CCB, vasoactive BB) may be efficacious in reducing the effects of early wave reflections. In such patients, more aggressive therapy to relax the vasculature and reduce central pulse pressure is recommended.
*Roman et al. Hypertension. 2007;50:197-203
Figure 1. Central Aortic Clinical Parameters
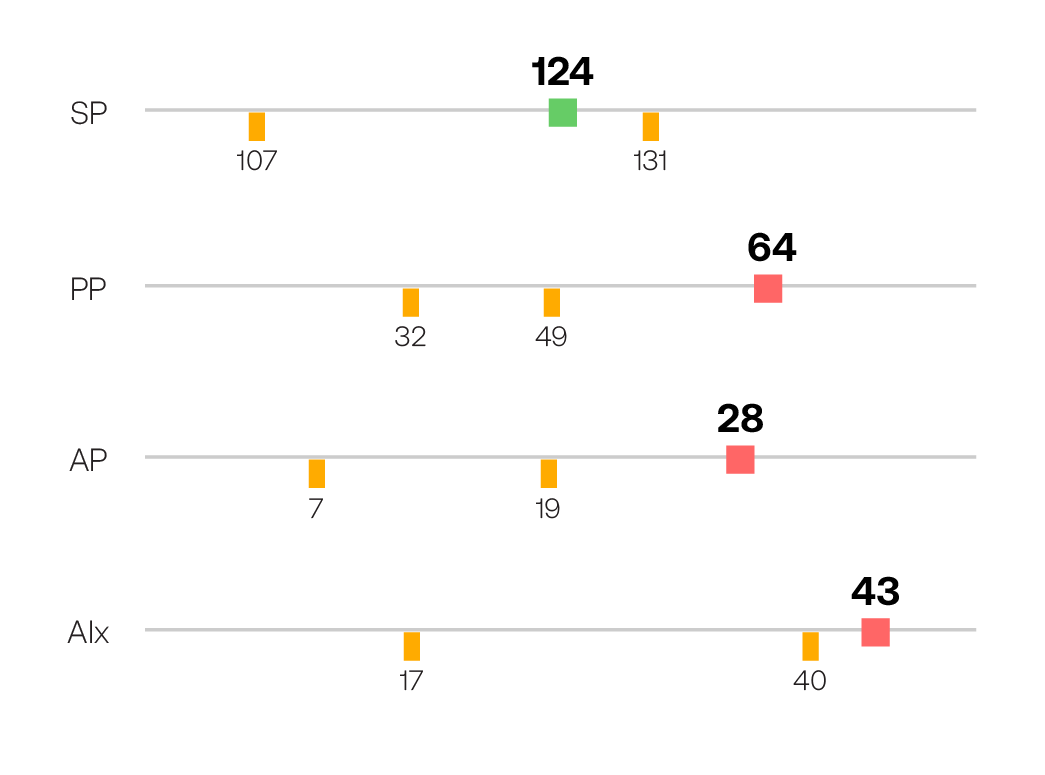
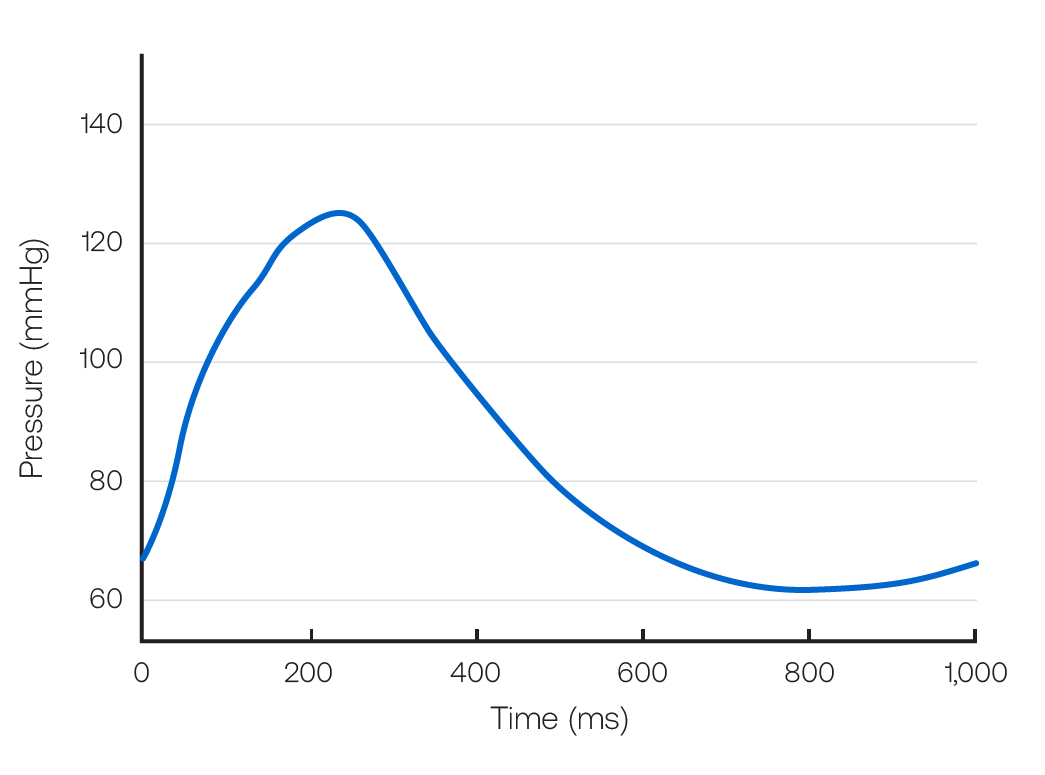
Figure 1b. Average Central Aortic Waveform
Other Case Studies
